- Home
- General Economy
- Monetary Policy & Turkey& ...
Monetary policy is a set of actions to control a nation’s overall money supply, steering the economy towards expansion or contraction. Monetary policy is usually set by a national central bank like the Federal Reserve System (FRS/FED) in the US or countries with harmonized monetary policies like the EU by the European Central Bank (ECB)
How does the money supply affect the economy?
Imagine a supply and demand, like any stock market or industry and replace the product with money.
When the money supply is increased through monetary policy, money loses its value (scarcity), leading to Inflation. In other words, everyone can start buying Ferraris with their money, so Ferrari ups its price to avoid a shortage. Mirror this effect in every industry, and the average price level in an economy increases hence Inflation.
The Opposite effect is true when the money supply is decreased.
What are the goals of monetary policy
Different Central Banks Set different goals to achieve:
For example, the US Federal Reserve declares its goals of “maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates.”
The European Central Bank’s goals revolve around stable prices, creating a positive spillover effect on job creation and economic growth.
Other central banks consider the export nature of the economy. For example, they may want to achieve more inflation to weaken their currency to produce cheaper, competitively priced exports (however, at the expense of the population if they are willing to exchange money or live abroad).
Regardless of individual Central banks, the main goal is to keep inflation stable between two–four per cent each year. This, however, requires the Central banks to cool down the economy when it rises above four and to stimulate it when it decreases under two, generally in the smoothest way possible.
What are the main tools used in monetary policy?
All of the below can be inverted to steer the money supply the reverse direction.
Changing Interest rates
By increasing interest rates, it costs more to borrow money; less money is borrowed leading to less money supply, decreasing inflation
Quantitative Easing/Tightening
The central bank can reduce the money supply by selling the assets it has purchased and placing the money in reserves or burning it.
Changing Reserve Requirements
Increasing reserve requirements means that banks must hold more money in their reserves. This means less money supply in circulation, decreasing inflation
Why is Turkey's Monetary Policy so Controversial?
Having understood the basics of monetary policy, we examine countries’ monetary policy response to inflation versus Turkey’s “odd” response. BOE has hiked rates by 0.75%, and the ECB has moved in tandem to contract the economy and decrease inflation. This is proven to be having an effect in the past few days reports on the level of credit have been reducing; however, the impact on price will be seen in roughly a year.
Turkey has done the complete opposite. Faced with one of the worst inflations in the eurozone, it has decided to go on rounds of interest rate cuts and other expansionary policies. This means that it is increasing its money supply in the face of inflation, which provides temporary relief for the high prices, but ultimately spirals into hyperinflation.
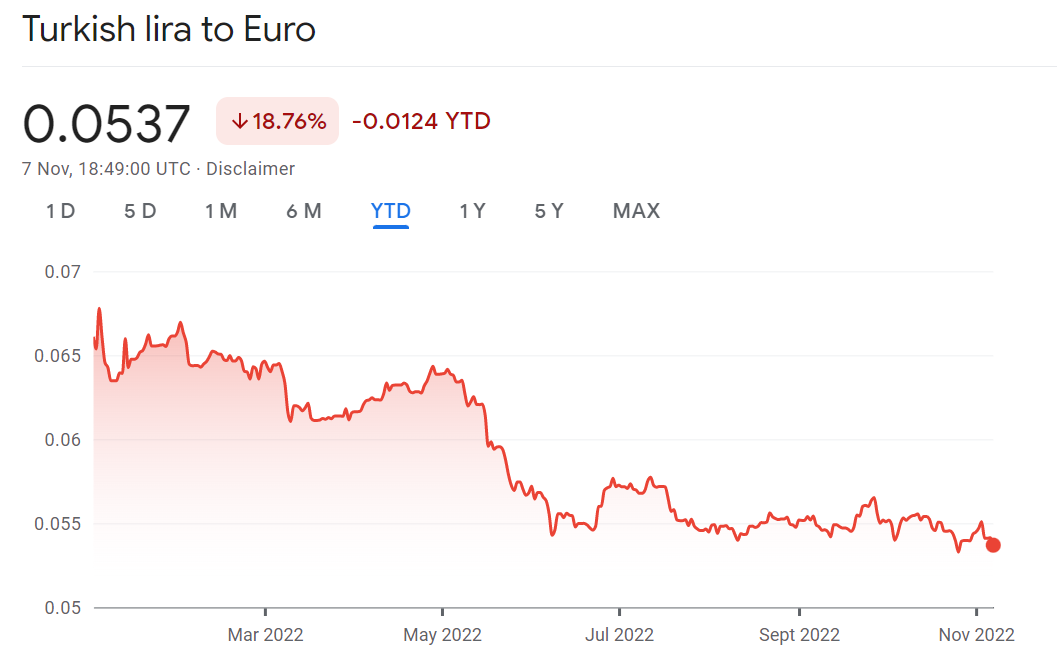
The result is clear: a much larger incidence of inflation in the Turkish Lira rather than in the Euro with a loss of 18.76% YTD in exchange rate.
What could be the motives?
Usually, a country weakens its currency to provide more competitively priced exports. However, Turkey is at an export deficit (it imports more than exports). Turkish president Erdogan has supported their monetary policy saying that interest hikes cause inflation (which is untrue to conventional economics) and that his economic policy will spur growth and employment. The latter is true. However, it is only a temporary effect of the money supply boost and will need additional stimulus to keep up the inflationary cycles.
Poll
Search
Recent Post
$APPL Equity Q2 2023 Report
- October 5, 2023
- 9 min read
Apple 2023 Executive Summary
- October 4, 2023
- 5 min read
M&A: Announced Pfizer Aquiring Seagen
- October 3, 2023
- 4 min read




